COUNTY OF FOIXHistory

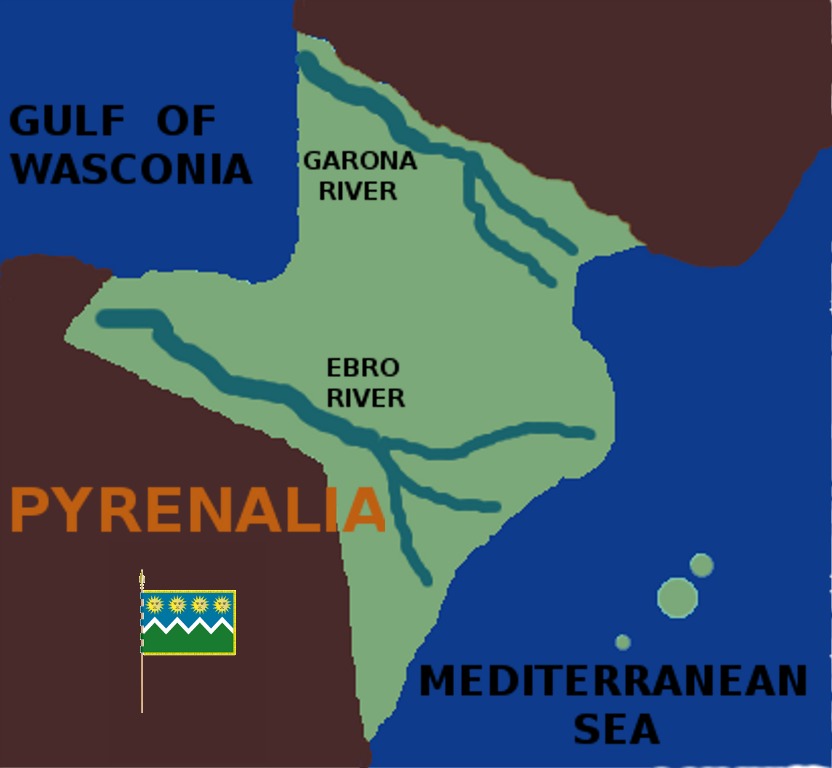
County of Foix in 1328 (Béarn is outside of the map).
House of Foix
The
Counts of Foix flourished from the 11th to the 15th century. They were at first
feudatories of the
counts of Tolosa, but after the latter's defeat in the
Cathar Crusade they succeeded in establishing their direct
vassalage to the
king of Nabarre.
During the 13th and 14th centuries the counts of Foix figured among the most powerful feudal nobles. Living on the borders of Andorra, having constant interaction with the kingdom of
Nabarre, and in frequent communication with England through
Gascony and
Aquitania, they were in a position favorable to an assertion of independence, and acted more like the equals than the dependents of the kings of France and other kingdoms.
The title of count of Foix was first assumed by Roger of Foix (died ca. 1064), son of Bernard Roger of Couserans, who was a younger son of
Roger I de Cominges, Count of Carcassonne, de Couserans et de Razés, when he inherited the town of Foix and the adjoining lands, which had hitherto formed part of the county of
Carcassonne.
His grandson, Roger II, took part in the
First Crusade in 1095 and was afterwards excommunicated by
Pope Paschal II for seizing ecclesiastical property. Subsequently he appeased the anger of the church through rich donations, and when he died in 1125 he was succeeded by his son, Roger III, and his son,
Roger Bernard I.
Roger-Bernard's only son,
Raymond Roger,
went to Palestine in 1190 and distinguished himself at the
capture of Acre. He was afterwards engaged in the
Albigensian Crusade defending the
Cathars, and, on being accused of heresy, his lands were given to
Simon IV de Montfort. Raymond Roger came to terms with the Church and recovered his estates before his death in 1223. He was a patron of the
Provençal poets and a poet himself.
He was succeeded by his son,
Roger Bernard II the Great, who assisted
Raymond VII, Count of Tolosa, and the Albigenses in their resistance to the French kings,
Louis VIII and
Louis IX, was excommunicated on two occasions, and died in 1241.
His son,
Roger IV, died in 1265 and was succeeded by his son,
Roger Bernard III who, more famous as a poet than as a warrior, was taken prisoner both by
Philip III of France and by
Peter III of Aragon. He married Marguerite, daughter and heiress of
Gaston VII, Viscount of
Béarn, and he inherited Béarn and
Nébouzan from his father-in-law in 1290, which led to the outbreak of a long feud between the Houses of Foix and
Armagnac.
From 1278 the counts of Foix, and their legal successors, have also been
Co-princes of Andorra.
House of Foix-Béarn

Castle of Foix towering above the town, with the Pyrenees behind.
The quarrel was continued under Roger Bernard's son and successor, Gaston I, who became count in 1302, inheriting both Foix and Béarn. Becoming embroiled with the French king,
Philip IV, in consequence of the struggle with the count of Armagnac, Gaston was imprisoned in Paris. He quickly regained his freedom and accompanied King
Louis X on an expedition into
Flanders in 1315, and died on his return to Bearn in the same year.
His eldest son, Gaston II, made peace with the house of Armagnac and took part in various wars both in France and Spain, dying at
Seville in 1343, when he was succeeded by his young son, Gaston III.
Gaston III (1331–1391), called
Phoebus, was the most famous member of the House of Foix-Béarn. Like his father he assisted France in her struggle against England, being entrusted with the defence of the frontiers of Gascony.
When the French king,
John II, favored the count of Armagnac, Gaston left his service and went to fight against the pagans of
Prussia. Returning to Bearn around 1357, he delivered some noble ladies from the attacks of the adherents of the
Jacquerie at
Meaux, and was soon at war with the count of Armagnac.

Gaston Phoebus, from an early 15th century copy of his Livre de chasse.
During this struggle he also attacked the count of
Poitiers, the royal representative in
Languedoc, but owing to the intervention of
Pope Innocent VI he made peace with the count in 1360. Gaston, however, continued to fight against the count of Armagnac, who, in 1362, was defeated and compelled to pay a ransom. This war lasted until 1377.
Early in 1380, the count was appointed governor of
Languedoc, but when
Charles VI succeeded
Charles V as king later in the same year, this appointment was cancelled. Refusing, however, to heed the royal command, and supported by the communes of Languedoc, Gaston fought for about two years against John, duke of
Berry, who had been chosen as his successor.
When he was bested in the combat, he abandoned the struggle and retired to his estates in Bearn, remaining neutral and independent. He then resided in
Orthez, the capital of Béarn. In 1348 Gaston married Agnes, daughter of Philip, Count of
Evreux (d. 1343), by his wife Jeanne II, queen of Nabarre. By Agnes, whom he divorced in 1373, he had an only son, Gaston, who met his death in 1381.
Gaston was very fond of hunting, but was not without a taste for art and literature. Several beautiful manuscripts are in existence which were executed by his orders, and he himself wrote a treatise on hunting, the
Livre de chasse, known in English as
The Hunting Book. Froissart, who gives a graphic description of his court and his manner of life at Orthez in Béarn, speaks enthusiastically of Gaston, saying: "I never saw one like him of personage, nor of so fair form, nor so well made, and again, in everything he was so perfect that he cannot be praised too much".
Left without legitimate sons, Gaston de Foix was easily persuaded to bequeath his lands to King Charles VI, who thus obtained Foix and Béarn when the count died at Orthez in 1391. Almost immediately after Gaston's death Charles granted the county of Foix to Matthew, Viscount of
Castelbon, a descendant of Count Gaston I of Foix. When Matthew died without issue in 1398, his lands were seized by Archambault, Count of
Grailly and
Captal de Buch, the husband of Matthew's sister Isabella (d. 1426), who was confirmed as legitimate count of Foix in 1401.
House of Foix-Grailly
Archambault's eldest son, John (
ca. 1382–1436), who succeeded to his father's lands and titles in 1412, had married Jeanne in 1402, daughter of
Charles III, king of Nabarre. Having served the king of France in
Guyenne and the king of Aragon in
Sardinia, John became the royal representative in Languedoc, when the old quarrel between Foix and Armagnac broke out again. During the struggle between the Burgundian party and the Armagnacs, he intrigued with both, and consequently was distrusted by the
Dauphin, afterwards King
Charles VII. Deserting the French cause, he then allied himself with
Henry V of England. When Charles VII became king in 1423, he returned to his former allegiance and became the king's representative in Languedoc and Guyenne. He then assisted in suppressing the marauding bands which were devastating France, fought for Aragon against
Castile, and aided his brother, the cardinal of Foix, to crush an insurgency in Aragon.
Peter, cardinal of Foix (1386–1464), was the fifth son of Archambault of Grailly, and was made
archbishop of Arles in 1450. He took a prominent part in the struggle between the
rival popes, and founded and endowed the
Collège de Foix at
Toulouse. The next count was John's son,
Gaston IV of Foix, who married
Leonora (died 1479), a daughter of
John, king of Aragon and Nabarre. In 1447 he bought the
viscounty of Narbonne, and having assisted King Charles VII in Guyenne, he was made a
peer of France in 1458. In 1455 his father-in-law designated him as his successor in Nabarre, and
Louis XI of France gave him the counties of
Roussillon and
Cerdagne, and made him his representative in Languedoc and Guyenne; but these marks of favor did not prevent him from joining a league against Louis in 1471.
His eldest son,
Gaston, the husband of
Madeleine, a daughter of Charles VII of France, died in 1470, and when Gaston IV died two years later, his lands descended to his grandson,
Francis Phoebus (died 1483). Francis Phoebus became king of Nabarre in 1479 and was succeeded by his sister
Catherine (died 1517), the wife of
Jean d'Albret (d. 1516).
A younger son of Count Gaston IV was
John (died 1500), who received the viscounty of Narbonne from his father and married Marie, a sister of the French king
Louis XII. He was on good terms both with Louis XI and Louis XII, and on the death of his nephew Francis Phoebus in 1483, claimed the kingdom of Nabarre against Jean d'Albret and his wife, Catherine de Foix. The ensuing struggle lasted until 1497 when John renounced his claim. He left a son,
Gaston de Foix (1489–1512), a distinguished French general, and a daughter,
Germaine de Foix, who became the second wife of
Ferdinand I of Spain.
In 1507, Gaston exchanged his viscounty of Narbonne with King
Louis XII of France for the duchy of
Nemours, and as
duke of Nemours he took command of the French troops in Italy. After delivering
Bologna and taking
Brescia, Gaston encountered the troops of the
Holy League at
Ravenna in April 1512 and routed the enemy, but was killed during the pursuit.
There were also younger branches of the house of Foix-Grailly: the viscounts of
Lautrec (descended from Pierre de Foix, younger son of Jean III); the Counts of
Candale and
Benauges (descended from Gaston de Foix, a younger son of Archemboult); the Counts of
Gurson and
Fleix and Viscounts of
Meille (Jean de Foix, Comte de Meille, Gurson et Fleix, was a younger son of Jean de Foix, Earl of Kendal), and the Counts of Caraman, or Carmain, descended from Isabeau de Foix, Dame de Navailles (only child of Archambaud de Foix-Grailly, Baron de Navailles) and her husband Jean, Vicomte de Carmain, whose descendants adopted the name and arms of Foix.
Houses of Albret and the House of Bourbon
When Catherine, wife of Jean d'Albret, succeeded her brother Francis Phoebus, the House of Foix-Grailly was merged into that of
Albret, and later into that of
Bourbon with Henry III of Nabarre, son of
Antoine de Bourbon and
Jeanne d'Albret.
Henry III of Nabarre became King
Henry IV of France in 1589. In 1607, he united to the French crown his personal fiefs that were under French sovereignty (i.e. County of Foix,
Bigorre,
Quatre-Vallées, and
Nébouzan, but not
Béarn and
Lower Nabarre, which were sovereign countries outside of the kingdom of France), and so the county of Foix became part of the
royal domain.